- Introduction
- What is Quantum Computing?
- Understanding Quantum Computing in Financial Contexts
- The Quantum Leap: Enhancing Security in Financial Transactions
- Quantum Computing’s Role in Risk Management and Analysis
- Accelerating Trading Algorithms with Quantum Computing
- Quantum in Banking Systems: A Case Study
- Overcoming the Challenges of Implementing Quantum Financial Systems
- The Future of Quantum Financial Systems: Trends and Predictions
- Expert Device Support for Quantum Financial Systems
- Conclusion: Embracing Quantum Computing in Finance
Introduction
Imagine a world where financial transactions happen in the blink of an eye, market predictions are eerily accurate, and cybersecurity is virtually unbreakable. Welcome to the quantum revolution in finance.
In this post, we will explore how quantum computing is transforming financial IT infrastructure and provide real-world examples of its impact.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing represents a revolutionary leap in computational power, operating on principles fundamentally different from classical computing.
Quantum computers typically receive inputs from classical computers, rather than independent inputs. This interaction between classical and quantum systems is an important aspect of how quantum computing is implemented in practice.
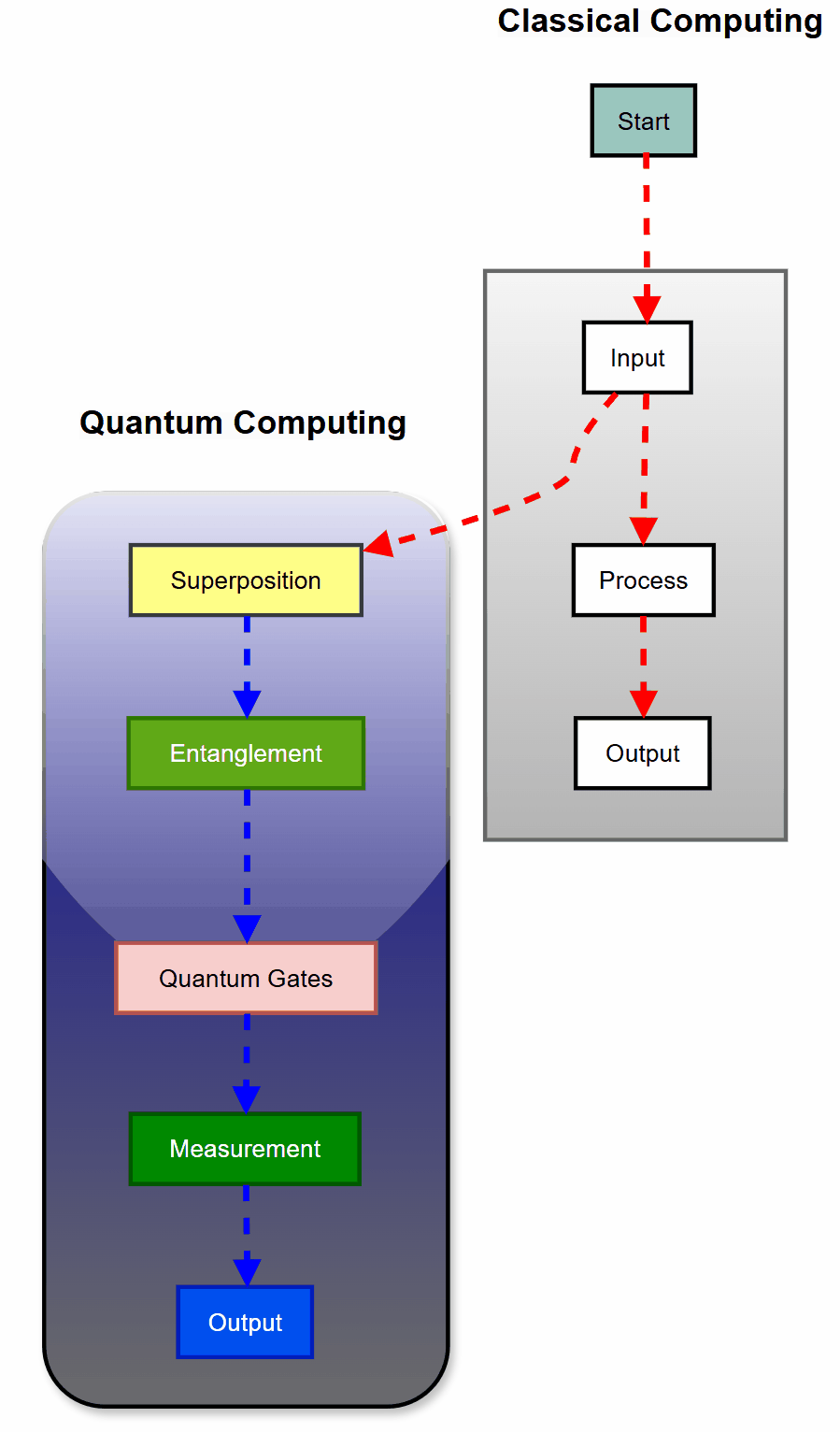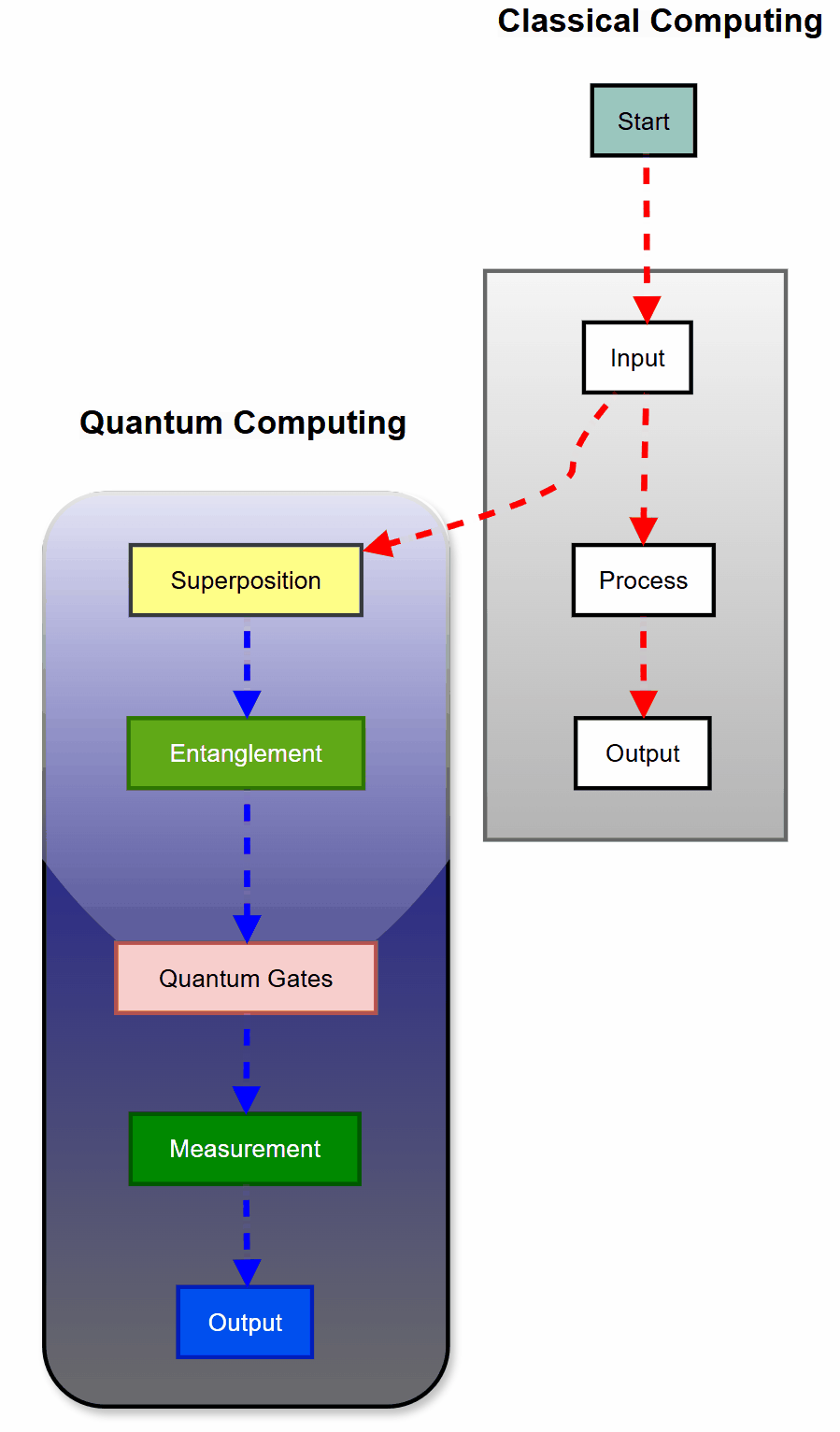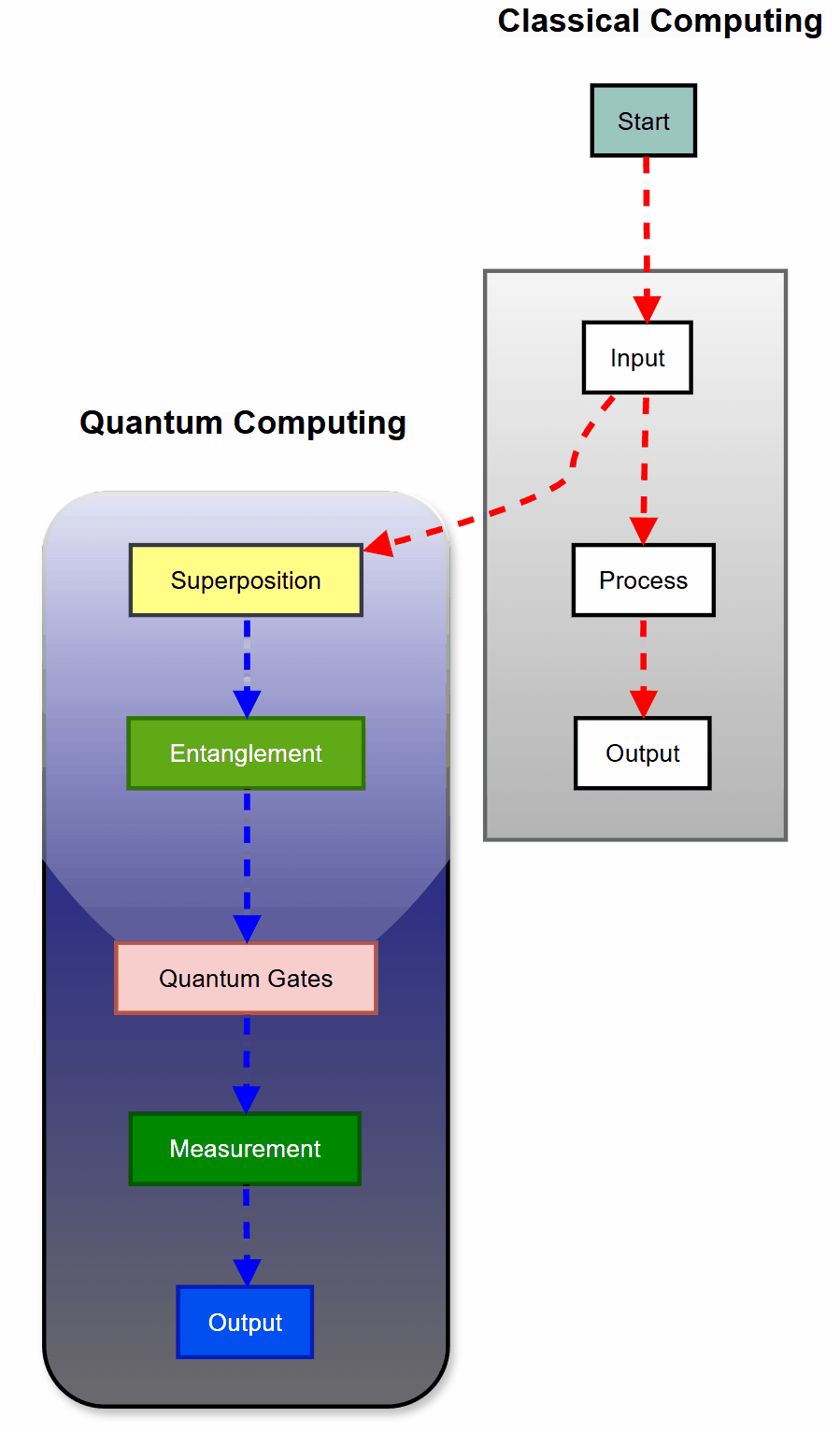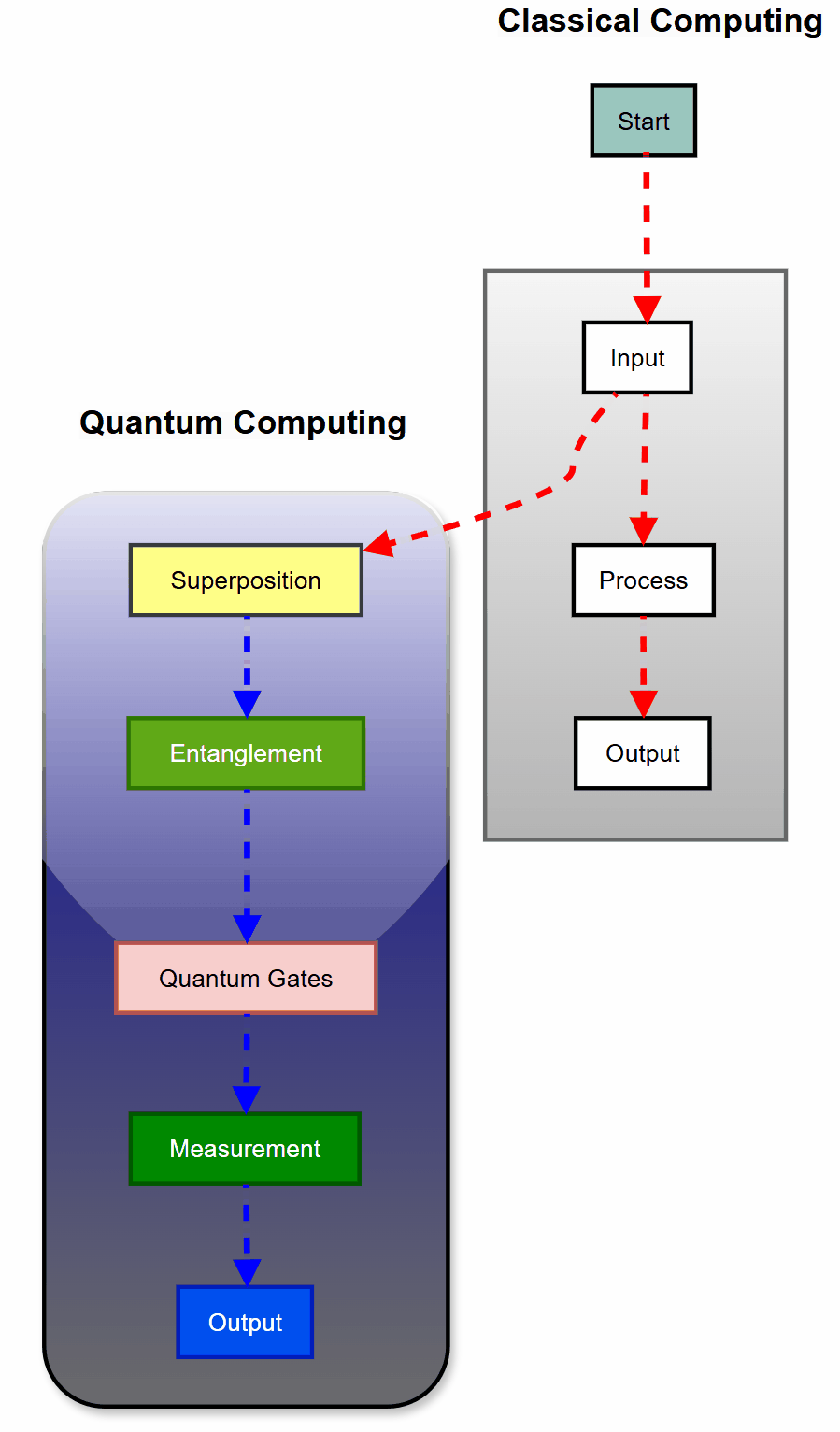
While classical computers use bits that are either 0 or 1, quantum computers leverage the bizarre properties of quantum mechanics to process information in ways previously thought impossible.
To understand quantum computing, we need to grasp a few key concepts that drives the technology.
Qubits
This is the basic unit of quantum information. Unlike classical bits, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously thanks to superposition.
Superposition
Unlike classical bits, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This is known as superposition.
Superposition allows qubits to be in a combination of 0 and 1 states at the same time, enabling quantum computers to process vast amounts of information in parallel.
Entanglement
Entanglement is a quantum phenomenon where qubits become interconnected, and the state of one cannot be described independently of the other, regardless of distance.
This enables quantum computers to perform certain calculations exponentially faster.
Quantum Gates
Operations that manipulate qubits, similar to logic gates in classical computing but leveraging quantum principles.
Measurement
The act of observing a qubit, which collapses its superposition into a classical state of either 0 or 1.
Interference
Quantum algorithms manipulate qubits to amplify correct solutions and cancel out incorrect ones, leading to more efficient problem-solving for specific tasks.
These properties enable quantum computers to perform certain calculations exponentially faster than classical computers, particularly in areas like cryptography, optimization, and simulating quantum systems.
While still in early stages, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize fields such as drug discovery, financial modeling, and artificial intelligence.
Understanding Quantum Computing in Financial Contexts

Processing Speed
At the forefront of technological innovation, quantum computing stands out as a groundbreaking force, particularly within the financial sector. This advanced computing paradigm promises not only an enhancement in processing speed but a redefinition of operational capabilities.
Quantum computing’s prowess lies in its ability to handle intricate computations exponentially faster than traditional systems. For financial entities, this translates into an unparalleled advantage in areas demanding heavy computational resources.
Tasks such as conducting sophisticated risk analysis, optimizing vast portfolios, and refining algorithmic trading models are accomplished with unprecedented efficiency and precision.
This quantum leap in computing power enables financial organizations to process vast amounts of data, uncovering insights and opportunities at a pace that sets them apart in the competitive marketplace.
Innovation and Scalability
Integrating quantum computing into financial IT infrastructure means opening new avenues for innovation and scalability. Traditional models of financial analysis and decision-making, constrained by the computational limits of classical systems, can now evolve.
With quantum computing, financial institutions can explore complex financial models, simulate market scenarios with greater fidelity, and devise strategies that were previously beyond reach. This shift not only accelerates the speed at which financial operations are conducted but also enhances the accuracy and depth of analytical processes.
Dynamic and Adaptive Systems
The adoption of quantum computing in financial contexts signifies a move towards more dynamic and adaptive IT infrastructures. Financial institutions are enabled to tackle computationally intensive tasks with agility, paving the way for new services and products that meet the evolving demands of the market.
As these organizations harness the power of quantum computing, they not only streamline existing operations but also create a framework for innovation that can sustain growth in an era of digital transformation.
The journey towards integrating quantum computing within financial IT landscapes is marked by the promise of transformative gains.
By empowering financial institutions with the tools to navigate complex computations effortlessly, quantum computing is not just an enhancement of technological capabilities—it’s a strategic asset that redefines the boundaries of financial services and operations.
The Quantum Leap: Enhancing Security in Financial Transactions

In the digital age where cybersecurity threats loom large, the finance sector is perpetually on the quest for the next level of security measures to protect sensitive data and financial transactions.
Quantum computing emerges as a game-changer in this scenario, offering a paradigm shift in how security is conceptualized and implemented within financial infrastructures.
Unlike traditional encryption methods, which could eventually be unraveled by the advancing computational power of classical computers, quantum encryption introduces a near-impenetrable layer of security, harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics.
Quantum encryption, or quantum key distribution (QKD), utilizes the quantum properties of particles like photons to secure communication channels. This method ensures that any attempt at eavesdropping alters the quantum state of the particles, making the intrusion detectable immediately.
For financial institutions, this means the ability to create a secure network for transmitting sensitive information where any breach attempt is not just thwarted but also flagged in real-time, providing an unprecedented level of security.
It propels the banking systems into a future where financial transactions, regardless of their complexity or the volume of data they encompass, are shielded by the principles of quantum physics.
As the financial industry navigates through the intricacies of digital transformation, the integration of quantum computing in transaction security offers a clear pathway to safeguarding assets in a manner that was previously deemed unachievable.
Quantum Computing’s Role in Risk Management and Analysis

Quantum computing is redefining the landscape of risk management and analysis within the financial sector, offering an unprecedented level of computational power and precision.
This emergent technology facilitates the deployment of quantum algorithms that can sift through complex market data and multifaceted risk factors with astonishing speed and accuracy.
Financial institutions stand at the brink of a new era, where quantum computing enables them to forecast risks and pinpoint market trends with a finesse that was previously unimaginable.
The intricate nature of financial markets demands a level of analysis that goes beyond the capabilities of classical computing systems. Traditional models, though effective to a degree, often struggle with the simulation of complex scenarios and the assessment of systemic risks in real-time.
For banks and investment firms, this quantum-powered leap in analytical capability translates into a more nuanced and detailed understanding of potential risks. They can now simulate economic scenarios with greater depth, analyzing outcomes under various conditions to identify potential vulnerabilities and opportunities.
The advent of quantum computing in risk management opens up new possibilities for creating more resilient financial products and services. Insurance companies, for instance, can leverage quantum algorithms to more accurately predict and price risks, tailoring their offerings to better meet the needs of their clients. Similarly, investment firms can use these insights to devise robust investment strategies that are optimized for long-term growth and stability.
As quantum computing continues to evolve, its role in transforming risk management and analysis is becoming increasingly pivotal. Financial institutions that adopt this technology are not just future-proofing their operations but are also laying the groundwork for a more secure, efficient, and innovative financial landscape.
Accelerating Trading Algorithms with Quantum Computing

In financial trading market, milliseconds can translate into significant financial gains or losses, and this is where quantum computing ushers in an era of unparalleled velocity and precision.
This groundbreaking technology equips trading systems with the ability to process complex algorithms at speeds unattainable by classical computing, enabling financial institutions to identify and act on market opportunities with an agility that was once thought impossible.
The field of algorithmic trading, characterized by its reliance on the rapid execution of orders, stands to benefit immensely from quantum computing. Traditional algorithms, while sophisticated, often grapple with the limitations imposed by classical computational models, particularly when navigating vast datasets or executing multifaceted trading strategies.
Quantum computing, with its ability to perform parallel calculations and assess probabilities in a fraction of the time, revolutionizes this landscape. It allows for the development of trading algorithms that can adapt in real-time, optimizing trading strategies to capitalize on market changes instantaneously.
Furthermore, the integration of quantum computing into trading systems is not just about speed; it’s about the depth of analysis. Quantum algorithms can delve deeper into market data, uncovering patterns and correlations that are obscure or hidden from classical algorithms. This enhanced analytical capability enables traders to make more informed decisions, reducing risks and improving the profitability of trading operations.
Quantum in Banking Systems: A Case Study

Exploring the forefront of quantum computing within the financial sector, several major financial institutions are actively involved in quantum computing, with the number likely to grow as the technology matures.
These firms, mainly in the banking sector have embarked on an ambitious journey to integrate quantum computing into their core banking systems, marking a significant milestone in the fusion of finance and quantum technology.
The firm’s pioneering initiatives in quantum computing are primarily focused on four critical areas: Portfolio Optimisation, Risk Management, Fraud Detection and System Security.
Portfolio Optimization
One of the leading commercial banks in the world, has been exploring quantum computing applications in finance. The bank has partnered with quantum computing experts to investigate how quantum computing could improve portfolio optimization.
Problem
Traditional portfolio optimization methods using classical computers struggle with the complexity of large-scale portfolios, especially when considering multiple objectives and constraints. As the number of assets and factors increases, the computational time grows exponentially.
Quantum Approach
The bank used a quantum algorithm called Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) to tackle the portfolio optimization problem. They formulated the problem as a quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) problem, which is well-suited for quantum computers.
Implementation
- Asset selection: They chose a subset of assets from their portfolio.
- Problem formulation: The team defined objective functions (e.g., maximizing returns, minimizing risk) and constraints (e.g., budget, diversification).
- QUBO mapping: They mapped the portfolio optimization problem to a QUBO format.
- Quantum circuit design: A quantum circuit implementing the QAOA was designed.
- Execution: The algorithm was run on Honeywell’s trapped-ion quantum computer.
- Result analysis: Outputs were analyzed and compared to classical methods.
Results
- The quantum approach found high-quality solutions for small to medium-sized portfolios.
- For larger portfolios, the quantum method showed potential for finding better solutions in less time compared to classical methods.
- The quantum algorithm demonstrated particular strength in scenarios with complex constraints.
Challenges
- Current quantum hardware limitations (e.g., number of qubits, noise) restricted the size of portfolios that could be optimized.
- Translating financial problems into quantum-ready formats required specialized expertise.
Future Outlook
The bank continues to invest in quantum computing research, anticipating that as quantum hardware improves, they’ll be able to optimize larger and more complex portfolios, potentially leading to better investment strategies and risk management.
Risk Management
A renowned global investment bank sought to improve its risk management capabilities, particularly in assessing complex derivative portfolios.
Challenge
Traditional risk models struggled with the computational complexity of simulating numerous market scenarios for large portfolios, leading to potential inaccuracies and delayed risk assessments.
Quantum Computing Solution
The bank partnered with a quantum computing firm to develop a quantum algorithm for Monte Carlo simulations – a key technique in financial risk assessment.
Implementation
- The team adapted Monte Carlo methods to run on a quantum computer, leveraging quantum parallelism.
- They used quantum amplitude estimation to accelerate the calculation of expected values and risk measures.
- The system was integrated with the bank’s existing risk management infrastructure.
Results
- Simulation speed: 100x faster than classical supercomputers for certain complex portfolios.
- Accuracy: Improved precision in Value at Risk (VaR) and Expected Shortfall calculations.
- Scenario analysis: Ability to run more market scenarios, enhancing stress testing capabilities.
Business Impact
- Faster risk assessment allowed for more frequent portfolio rebalancing.
- Improved accuracy in risk measures led to optimized capital allocation.
- Enhanced ability to comply with regulatory stress testing requirements.
Challenges and Limitations
- High costs associated with quantum hardware and expertise.
- Limited availability of quantum computers with sufficient qubits.
- Need for ongoing algorithm refinement as quantum technology evolves.
Future Outlook
The bank plans to expand quantum computing applications to other areas of risk management, including credit risk modeling and fraud detection.
Fraud Detection
Background: One of the global commercial and investment banks was facing increasing challenges with credit card fraud, losing millions annually. Traditional classical computing methods were struggling to keep up with sophisticated fraud techniques.
Quantum Computing Solution: The bank partnered with a quantum computing firm to develop a quantum-enhanced fraud detection system.
Key components
- Quantum machine learning algorithms
- Quantum-classical hybrid architecture
- Real-time transaction processing
Implementation
- Quantum algorithms were used to analyze complex patterns in transaction data
- The system could process vast amounts of data faster than classical methods
- Real-time scoring of transactions for fraud probability
Results
- 35% improvement in fraud detection accuracy
- 50% reduction in false positives
- $10 million saved in prevented fraud losses in the first year
Challenges
- High initial costs for quantum hardware and expertise
- Integration with existing banking systems
- Ongoing refinement of quantum algorithms
Future Outlook
The bank plans to expand the use of quantum computing to other areas of risk management and financial modeling.
System Security
Background
As quantum computers advance, traditional encryption methods used in online banking are becoming increasingly vulnerable. In response, a major international bank decided to implement quantum-resistant cryptography to protect its digital infrastructure and customer data.
Challenge
The bank needed to upgrade its security protocols to defend against potential quantum computer attacks while maintaining system performance and user experience.
Solution
The bank partnered with a quantum computing security firm to implement the following measures:
- Quantum-resistant algorithms
- Replaced RSA and ECC with post-quantum cryptography algorithms like lattice-based cryptography for key exchange and digital signatures.
- Implemented hash-based signature schemes for software updates and code signing.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD)
- Deployed QKD systems for secure communication between the bank’s data centers.
- Utilized quantum random number generators for enhanced key generation.
- Hybrid cryptography approach
- Implemented a dual system using both classical and quantum-resistant algorithms to ensure backward compatibility and gradual transition.
- Cryptographic agility
- Developed a flexible cryptographic infrastructure allowing for quick updates as new quantum-resistant algorithms emerge.
Implementation
The bank rolled out these changes in phases:
- Testing and integration (6 months)
- Tested quantum-resistant algorithms in a sandbox environment.
- Integrated new systems with existing infrastructure.
- Limited deployment (3 months)
- Implemented changes for a small group of high-value customers and internal systems.
- Full-scale deployment (1 year)
- Gradually rolled out quantum-resistant cryptography across all online banking services.
- Ongoing monitoring and updates
- Continual assessment of emerging quantum threats and algorithm effectiveness.
Results
- Enhanced security: The bank significantly reduced its vulnerability to potential quantum computer attacks.
- Improved customer trust: Marketing the advanced security measures led to increased customer confidence.
- Regulatory compliance: The bank positioned itself ahead of anticipated regulations on quantum-safe cryptography.
- Performance impact: Initial concerns about system slowdowns were mitigated through optimized implementations and hardware upgrades.
The integration of quantum computing in the IT structure of these firms serves as a vivid illustration of the transformative potential of this technology in banking. It not only highlights the firm’s commitment to innovation and excellence but also sets a precedent for the financial industry at large.
This case study exemplifies how embracing quantum computing is not merely an option but a strategic imperative for banks seeking to thrive in the era of digital finance.
Overcoming the Challenges of Implementing Quantum Financial Systems

Embarking on the quantum computing journey within the financial landscape presents its unique set of complexities and hurdles. Notably, the integration of quantum financial systems into existing IT infrastructures poses a sophisticated challenge that institutions must navigate with prudence and strategic foresight.
High CAPEX and OPEX
The lofty price tag associated with quantum hardware, the scarcity of quantum computing expertise, and the intricate process of transitioning from classical computing frameworks are among the pivotal challenges that loom large on the horizon.
The cost of acquiring and maintaining quantum computing hardware is indeed significant, necessitating a well-considered investment strategy. Financial institutions must weigh the long-term benefits of enhanced computational power and security against the initial financial outlay.
Innovative financing models and partnerships with quantum computing firms may provide a viable path forward, enabling access to quantum technologies without the burden of outright ownership.
Developing Quantum Talent and Expertise
The specialized nature of quantum computing demands a high level of expertise, which is currently in short supply. Cultivating an ecosystem of quantum literacy within an organization is essential.
This may involve investing in training programs to upskill existing staff or attracting quantum computing talents who can navigate the complex quantum landscape. Collaborations with academic institutions and research centers can also bridge the knowledge gap, fostering an environment of continuous learning and innovation.
Change Management
Transitioning from classical to quantum systems introduces a complexity that cannot be understated. It requires a thoughtful integration strategy that considers compatibility, scalability, and security.
Pilot projects and phased rollouts can allow for the gradual assimilation of quantum technologies, minimizing disruptions to existing operations. These initiatives offer invaluable insights, allowing institutions to refine their approach based on real-world experience.
Addressing these challenges head-on is pivotal for financial institutions keen on harnessing the transformative potential of quantum computing.
Through strategic investment, talent development, and mindful integration, the journey toward quantum-enabled financial systems can be navigated with confidence, unlocking new dimensions of efficiency, security, and competitive advantage in the ever-evolving digital finance landscape.
The Future of Quantum Financial Systems: Trends and Predictions

As we peer into the horizon of financial technologies, quantum computing heralds a new epoch marked by astonishing innovations and possibilities. The trajectory of this emergent technology suggests several compelling trends poised to redefine the essence of financial operations and services.
Quantum Machine Learning
The integration of quantum machine learning stands as a beacon of progress, promising to refine decision-making processes and enhance predictive analytics with unprecedented precision.
This facet of quantum computing will enable financial institutions to unearth deep insights from complex datasets, thereby improving investment strategies and customer experiences.
Quantum Cryptography
Equally transformative is the growing field of quantum cryptography, which is set to fortify the financial sector’s defenses against cyber threats.
With quantum-resistant algorithms, institutions will navigate the digital landscape with fortified confidence, securing assets and transactions against the most advanced cyber threats. This evolution in cybersecurity measures is not just a step but a leap towards ensuring the integrity and trustworthiness of financial systems on a global scale.
Quantum Finacial Modelling
Quantum financial modeling emerges as a critical trend, offering a new lens through which market dynamics and economic scenarios can be analyzed with remarkable depth.
This technology will allow for more precise risk assessments and the development of financial products tailored to meet the sophisticated needs of today’s market.
Financial entities will be equipped to simulate and predict market behaviors with a level of detail and accuracy that was previously unfathomable, paving the way for more strategic investment decisions and policy formulations.
The convergence of these quantum computing trends signifies a monumental shift towards more efficient, secure, and intelligent financial infrastructures. Institutions at the vanguard of adopting these quantum capabilities will not only lead in innovation but also set new standards for excellence in the financial sector.
As quantum computing continues to evolve and intersect with finance, it beckons a future where the full spectrum of financial services is transformed, elevating both the industry and the customer experience to unparalleled heights.
Expert Device Support for Quantum Financial Systems

Navigating the intricate journey of integrating quantum computing into the financial landscape requires not just a vision for innovation but a partnership with those who possess the expertise to bring such a vision to life.
Expert device support becomes indispensable in this context, offering a guiding light through the complexities of quantum technology. Tailored support services, provided by specialists in the field, play a crucial role in ensuring that financial institutions can fully harness the power of quantum computing, transforming potential hurdles into steppingstones towards success.
Professional services specializing in quantum technology offer a comprehensive suite of support that encompasses guidance on selecting the right quantum systems, customized training for teams to adeptly utilize these systems, and troubleshooting to address any operational challenges swiftly.
These experts stand at the confluence of theoretical knowledge and practical experience, making them uniquely equipped to help financial institutions navigate the quantum technology with confidence and strategic acumen.
Expert support extends beyond mere technical assistance; it encompasses a partnership that fosters continuous learning and adaptation in the fast-evolving domain of quantum computing. Financial institutions that engage with such support services are better positioned to leverage quantum computing as a dynamic tool for growth, navigating the future of finance with agility and foresight.
In this collaborative approach, the complex becomes manageable, and the cutting-edge becomes accessible, ensuring that financial institutions can leverage quantum computing to its fullest potential.
Conclusion: Embracing Quantum Computing in Finance

As we navigate the frontier of technological innovation, it’s clear that the integration of quantum computing within the finance sector marks a pivotal leap toward unprecedented efficiency, security, and strategic advantage.
The journey towards embracing this advanced computing technology is not merely about adopting new technology; it’s about reshaping the future of financial operations and services to meet the evolving demands of the global marketplace.
Quantum computing offers a unique opportunity for financial institutions to redefine their approach to complex challenges, from enhancing cybersecurity measures to revolutionizing risk management and trading algorithms. By tapping into the vast potential of quantum mechanics, banks and financial entities can unlock new dimensions of speed, precision, and insight, positioning themselves at the forefront of the digital transformation.
In embracing quantum computing, the finance sector opens the door to a future where financial services are more secure, decisions are more informed, and market opportunities can be seized with unparalleled agility. The transition to quantum financial systems is not without its challenges, but the rewards promise to redefine what’s possible in the realm of finance, offering a clear competitive edge to those who dare to lead the charge into this new era of digital excellence.


Leave a comment